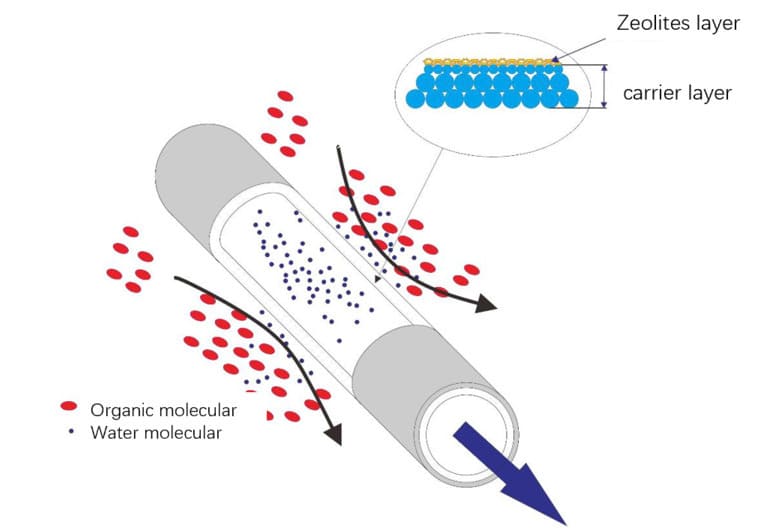
Pervaporation is a new technology of membrane separation and removal of water from industrial solvents.
Compared with distillation or rectification or other traditional separation technologies, pervaporation has outstanding advantages of high efficiency, low consumption, high recovery, convenient operation, safety, and environmental protection features, etc.
When the mixture liquid flows upstream of the membrane, the permeable components are selectively dissolved and adsorbed by the membrane, diffuse with the membrane, and flowthrough the membrane under the drive of the differential steam pressure on both sides of the membrane, and will be vaporized and collected in the membrane downstream, achieving the purpose of separation.
The pervaporation membrane separation process is working with high performance under conditions of PH6·5-8·5, DD<5us/cm, no salt crystals, no viscous macromolecules, it is especially suitable for separation and purification of azeotropes and near boilers that cannot be solved by distillation columns.
How to Ensure the Dehydration Performance?
The water content of the feed liquid directly affects the dehydration performance of the membrane module, and the diffusion rate of the components in the membrane is related to the composition of the material.
Therefore, the separation performance of pervaporation is closely related to the composition of the feed liquid.
Changes in the composition of the feed liquid will affect the separation performance.
For example, when the feed material contains strong polar solvents, the equipment’s separation performance including processing capacity, and outlet product water content will change.
Generally, when the concentration of preferentially permeating components in the feed liquid increases, the total amount of permeation will also increase.
However, under the condition that the performance and area of the membrane are fixed, the increase of the water content in the material will increase the water content of the product simultaneously.
Only reducing the feeding amount of the device ensures the quality of the product.
Material Liquid Testing Items and Methods
Raw material requirements:
the raw material to be treated and separated shall be organic solvent, colorless, clear, and transparent.
There shall be no stratification, and water content is ≤30wt.%, if it is more than 30% the membrane life will be shortened.
The feed pH range shall be 6.5~8.5, conductivity shall be <5μS/cm, and chloride ion content <20ppm.
No pigment, salt, sugar, colloid, acidic, alkaline components, or other substances that may pollute the equipment and membrane materials,
No residue or discoloration after evaporation, and should keep the raw material indicators normal and stable for a long time.
The raw material testing methods shall be determined by both parties as follows.
1. Moisture Determination
Determination of moisture content in chemical products with the Karl-Fischer method (general method) of detection according to GB/T 6283-2008, the process should be strictly operated to avoid the introduction of moisture and lead to determination errors.
2. Conductivity Determination
Using electrical conductivity meter testing method as per GB/T 11007-2008.
(1) the material liquid with high solubility of water (solvent phase water content ≥ 10%) and miscible with water.
Water content ≥ 10%: direct detection of electrical conductivity
water content ≤ 10%: add purified water to enrich the water content ≥ 10% and make detection of conductivity.
(2) the material solution with low water solubility (add water will stratification, and solvent phase water content ≤ 10%)
solvent and water 1:1 mixing and stirring, take the aqueous phase to analyze the conductivity.
Note: the purified water used shall be of conductivity ≤ 2; 6.5 ≤ pH ≤ 7.5.
3. pH Determination
Using the general rules of testing provisions of GB/T9724-2007 for chemical reagent pH determination.
(1) For the material solution of high water solubility (solvent phase water content ≥ 10%) and miscible with water.
Water content ≥ 10%: direct detection of pH
water content ≤ 10%: add purified water to enrich the water content of ≥ 10% and detect the pH.
(2) For the material solution of low water solubility(add water and stratification, and solvent phase water content ≤ 10%)
Mix solvent and water 1:1 and stir, and take the aqueous phase to analyze pH.
Note:
(1) The purified water shall be of conductivity ≤ 2; 6.5 ≤ pH ≤ 7.5
(2) the use of pH test paper to determine the pH value of the material solution, can not be used as the basis for the determination of the nature of raw materials.
4. Organic Component Determination
The use of national or industry standards, or the parties to determine by mutual agreement.
5. Impurities Determination
Take 1L into the membrane system as the raw materials for distillation, control the distillate extraction rate <15ml/min, the required distillation kettle residue <10ml, there shall be no significant change in color compared with raw materials, and continue to distill the residue, there is no paste or solid residue generated.
We are providing the complete engineering service and assembly unit of equipment to meet your process production targets.